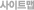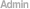H > 서비스 > Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) >Whole genome resequencing
Whole genome resequencing
Whole genome resequencing ?
Sequencing 기술이 고도로 발전함에 따라, 전체 genome이 밝혀진 종의 개수가 급속도로 늘어나고 있습니다. 이렇게 전체 genome이 밝혀진 종을 대상으로 특정 개체간의 변이를 분석하기 위해 whole genome resequencing을 수행하게 됩니다.
Sequencing 결과를 기존의 reference sequence와 비교하여, 특정 개체의 SNP, InDel, SV, CNV 등의 variation을 밝혀낼 수 있습니다. Whole genome resequencing의 가장 큰 활용 분야는 variation 연구로 인식되고 있습니다.
적용 분야
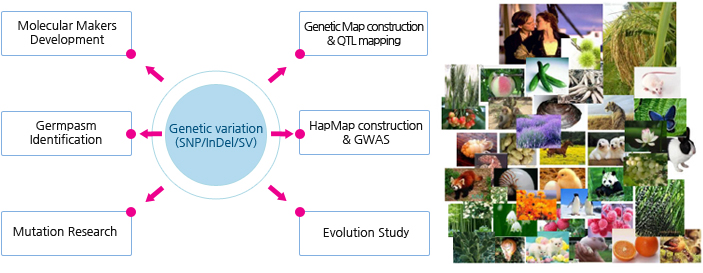
Bioinformatics 분석 Workflow
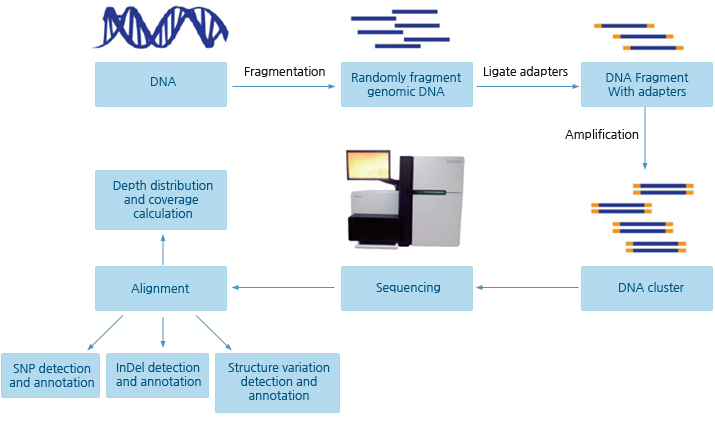
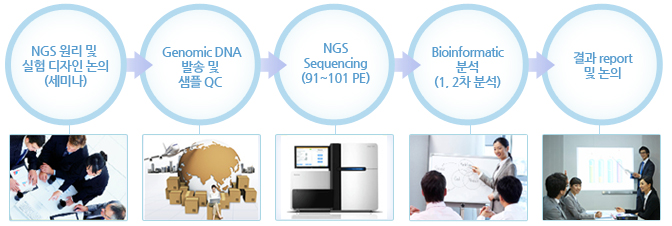
Whole genome resequencing - 실험 진행 과정
Sample requirements
| concentration | Concentration (ng/㎕) | Quality | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Genomic DNA | > 6㎍ (in general) | > 50 | OD(260/280)>1.8 is highly recommended |
| > 30㎍ (high GC bacteria) | > 50 |
Sequencing Strategy
| 91 ~ 101 PE (paired ends) sequencing |
Bioinformatic analysis - contents
| contents | |
|---|---|
| 1차 분석 (individual일때) |
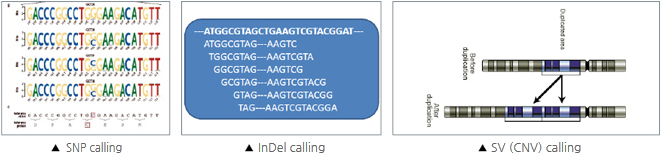
1. Data filtering (removing adaptors contamination and low-quality reads from raw reads) 2. Alignment and Summary of data production (Based on item 1) 3. SNP calling, annotation and statistics (Based on item 1&2) |
| 2차 분석
(individual일때) |
4. InDel calling, annotation and statistics 5. SV calling, annotation and statistics 6. CNV calling, annotation and statistics 7. Known phenotypic or disease risk variant screen 8. Genetic ancestry analysis > |
| 3차 분석 (population일때) |
9. Population SNP calling 10. Unbiased population frequency estimation (based on population SNPs) 11. Population InDel calling 12. Haplotype Analysis 13. Demographic Analysis (high-risk) 14. Population structure and Phylogenetics cluster analysis 15. Selection signals (middle-risk, the turnaround time may be changing according to different circumstances) |