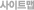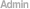H > 서비스 > Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) > Metagenomic survey
Metagenomic survey
Metagenomic Survey ?
특정 환경 및 시료 (stool, body fluid) 내에 존재하는 세균총의 동정, 분류 및 기능유전체 분석에 사용되는 기법입니다. 시료내의 미생물의 모든 genomic DNA를 분리하여 전체 DNA를 sequencing한 후, 결과 data를 assemble하여 시료내 세균총을 동정/분류하는 방법입니다. 시료내에서 genomic DNA를 직접 추출하므로, 균주 배양이 불가능한 균주도 모두 동정할 수 있게 됩니다. 또한, metagenomic survey 방법을 이용하면 동정된 균주의 유전자 기능 annoation 및 유사도 분석 및 pathway analysis도 함께 수행됩니다.
적용분야
- Metagenomics
- Microorganism classification
- Microorganism population study
- Species identification
- Gene function annotation
- Association study / pathway analysis
Metagenomic survey vs. 16s rDNA tagging
| Sequencing target |
Sequencing methods |
Data | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 16s rRNA tagging |
16s rRNA hypervariable regions |
Roche 454 | 1.Taxonomic classification
2.OTU analysis
|
| Whole genome metagenomic survey |
Whole bacterial genomes |
Illumina HiSeq | 1.Species identification
2.Gene prediction
3.ORF/functional annotation |

ChIP-Seq - 실험 진행 과정
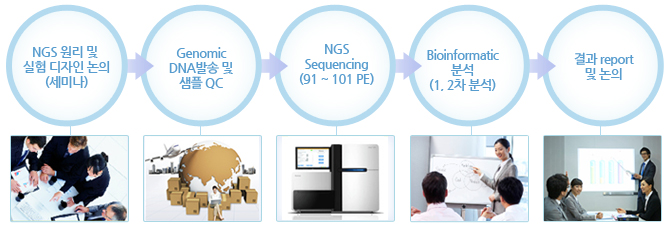
Sample requirements
| concentration | Concentration (ng/㎕) | Quality | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Genomic DNA | > 5㎍ (in general) | > 50 | OD(260/280)>1.8 is highly recommended |
Sequencing Strategy
| 91 ~ 101 PE sequencing |
Bioinformatic analysis - contents
| contents | |
|---|---|
| 1차 분석 |
1. Remove the low-quality reads 2. Remove the adapters 3. Statistics for host contamination rate (If host genome sequence is known) 4. Assembly 4.1 Statistics of assembly results 4.2 Statistics of Contigs' length distribution 5. Complexity analysis of sample 5.1 Statistical table of reads usage for assembly 5.2 Kmer level estimate and GC-depth analysis 5.3 Statistical for reads alignment to known bacterial genome database, RDP database, fungal genome database, human gut gene catalogue etc. |
| 2차 분석 | 1. Species classification analysis and functional annotation 2. Primary comparative analysis: 3. Advanced comparative analysis |