H > 서비스 > Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) >MeDIP-Seq
MeDIP-Seq
MeDIP-Seq ?
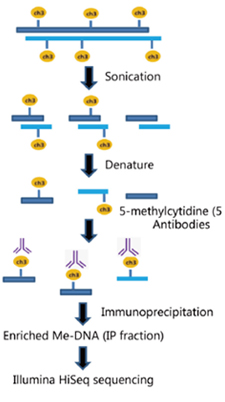
Epigenetics의 한 분야인 methylation 현상을 연구하기 위해 수 많은 방법이 개발되어 왔습니다. MeDIP (Methyl-binding domain-IP)는 methylated DNA fragment만을 enrichment하는 방법입니다.
MeDIP-enriched DNA를 이용하여 whole genome resequencing을 수행하면 비교적 적은 비용으로 methylated DNA에 대한 whole genome profiling을 분석할 수 있습니다.
적용분야
- Genome-wide methylation study
- differential methylated region (DMR) 탐색
- gene expression data와 연계한 통합 분석
- cancer biomarker discovery
실험 Workflow
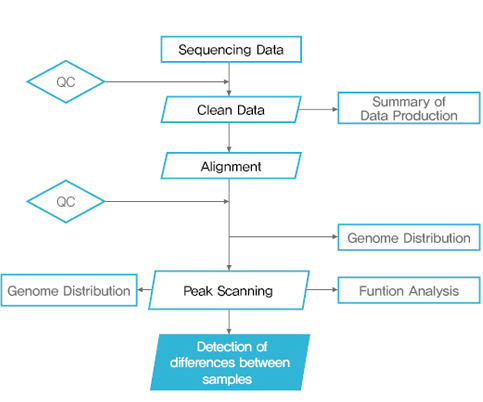
Bioinformatics 분석 Workflow
MeDIP-Seq - 실험 진행 과정
Sample requirements
| concentration | Concentration (ng/㎕) | Quality | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Genomic DNA | > 5㎍ (in general) | > 50 | OD(260/280)>1.8 is highly recommended |
Sequencing Strategy
| 50 PE (paired ends) sequencing (50 SE, 91 PE and 101 SE/PE sequencing (if needed)) |
Bioinformatic analysis - contents
| contents | |
|---|---|
| 1차 분석 |
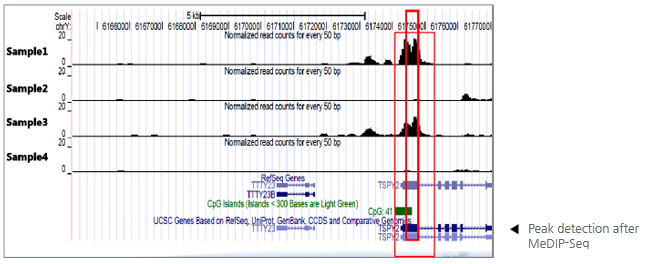
1. Data Filtering 2. Reads Alignment 3. Distribution of Uniquely Mapped Reads 4. Peak Scanning and Genome-wide Distribution |
| 2차 분석 | 5. Difference Analysis of Multi-samples 5.1 Differential Analysis 5.2 GO Enrichment Analysis and KEGG Pathway Analysis 6. Combined Analysis of MeDIP-Seq with small RNA-seq 7. Combined analysis of MeDIP-Seq with mRNA expression data 8. Combined Analysis of MeDIP-Seq with small RNA-seq and mRNA Expression Data |